The enactment of data privacy laws at the state level is driven by a combination of factors, including the need to protect consumers, respond to technological advancements, align with global standards, and address the evolving landscape of data usage and protection. As these laws continue to evolve, there is a growing call for a comprehensive federal approach to harmonize and streamline data privacy regulations across the United States.
Global privacy regulations, such as the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), have influenced the push for stronger data protection measures at the state level. States aim to align their regulations with international standards to facilitate cross-border data transfers. In the absence of comprehensive federal data privacy legislation in the United States, individual states have taken the initiative to pass their own laws. This has led to a patchwork of regulations, prompting calls for a federal framework to provide consistency and clarity.
Ethical, Fair & Transparent Data Processes
The monetization of consumer data by businesses has raised ethical questions about how personal information is used for profit. Data privacy laws seek to establish guidelines for fair and transparent data practices, including limitations on data monetization.
Provisions to Prevent Discrimination
Some data privacy laws include provisions to prevent discriminatory practices based on individuals’ personal information. This is particularly relevant in the context of algorithms and artificial intelligence systems that may perpetuate biases.
States with Strict Data Protection Policies
There are eleven states currently (Nov 2023) with extensive data privacy laws in place: California, Virginia, Connecticut, Colorado, Utah, Iowa, Indiana, Tennessee, Oregon, Montana, and Texas.
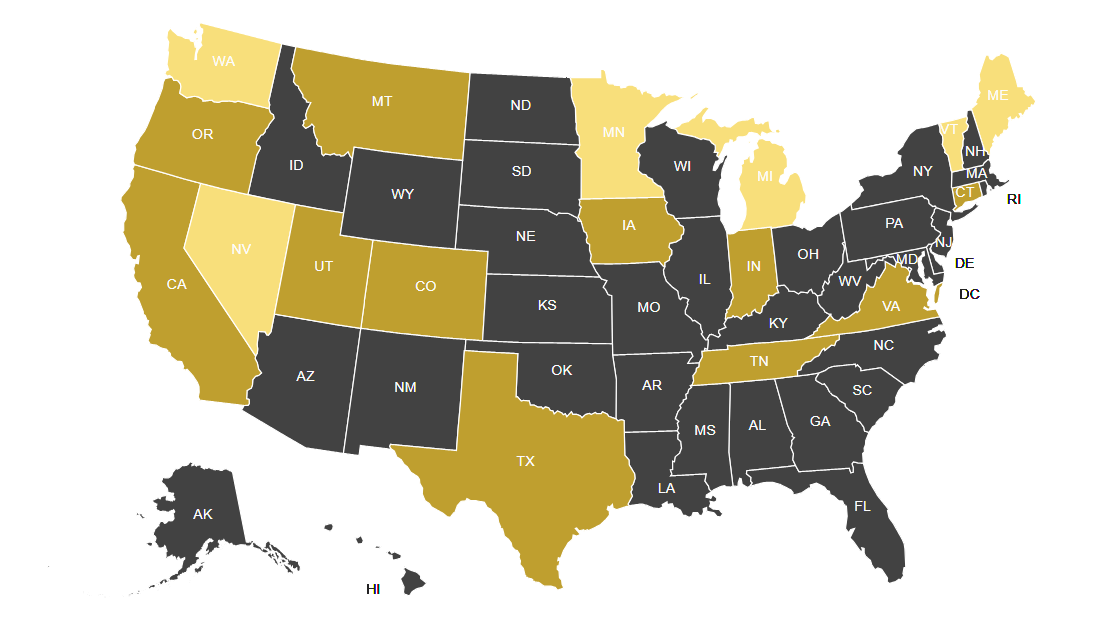
Here is a list of 12 states that introduced privacy bills in 2023:
- Illinois
- Louisiana
- Massachusetts
- Minnesota
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New York
- North Carolina
- Oklahoma
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- Vermont
To state up to date on privacy laws by state, you can go here.
Below are some examples of provisions enacted or proposed by various states.
- Establish privacy rights and business requirements for collecting and selling personal information
- Consumers having a right to access their data and request that their personal information be deleted by businesses
- Require companies to conduct data protection assessments to process personal data for targeted advertising and sales purposes
- Enable consumers to confirm that a business has collected their personal data, obtain a copy of the information, and request that inaccuracies be corrected
- Limit the collection of personal data to only “adequate, relevant, and reasonably necessary” information
- Provisions on biometric data, sensitive and personal data, and children’s data protections
Companies with Alleged Data Privacy Violations
Several companies have faced legal action or lawsuits related to alleged violations of marketing data policies.
Facebook (Meta): Facebook has faced multiple lawsuits and regulatory actions related to privacy and data protection issues. The Cambridge Analytica scandal in 2018, where personal data of millions of users was improperly accessed for political profiling, led to legal challenges and regulatory fines.
Google: Google has been subject to various legal actions related to data privacy. In 2020, Google faced a lawsuit for allegedly tracking users’ activities in “incognito” mode without their consent. The company has also faced legal challenges in Europe under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Zoom Video Communications: Zoom faced a class-action lawsuit in 2020 for allegedly sharing user data with Facebook without proper disclosure or consent. The lawsuit highlighted concerns about user privacy and data-sharing practices.
TikTok: TikTok has faced legal challenges related to data privacy, particularly regarding its handling of user data, data collection practices, and potential sharing of information with the Chinese government. Multiple countries, including the United States, have expressed concerns and initiated investigations.
Clearview AI: Clearview AI, a facial recognition technology company, faced legal challenges over its data scraping practices. The company scraped public images from various online sources to build a large facial recognition database, leading to concerns about privacy violations.
Oracle and Salesforce: In 2021, a privacy group filed complaints against Oracle and Salesforce with European data protection authorities, alleging that their real-time bidding systems violated the GDPR by processing personal data without proper consent.
Resources
https://pro.bloomberglaw.com/brief/state-privacy-legislation-tracker/
https://www.ncsl.org/technology-and-communication/state-laws-related-to-digital-privacy